과제 > this keyword
Original Code
var person = {
name: "홍길동",
birthday: "030219",
age: 30,
pId: "1234567",
fullId: function() {
return this.birthday + this.pId;
}
};
person.fullId() // 0302191234567
person.fullId; // function () { return this.birthday + this.pId; }
//생성자(constructor)를 이용한 객체 생성
var day = new Date(); // new 연산자를 사용하여 Date 타입의 객체를 생성함.
console.log("올해는 " + day.getFullYear() + "년입니다.");
Edited Code
var person = {
name: "홍길동",
birthday: "030219",
age: 30,
pId: "1234567",
fullId: function() {
return birthday + pId;
}
};
위 코드에 따라 person 객체 안에 있는 fullID 함수를 아래처럼 호출하면 ReferenceError가 발생된다.
person.fullId();
RESULT
C:\Users\Eunice\OneDrive - Sogang\바탕 화면\git\ai_webdev\js_ts\this_reference_error\8_object.js:7
return birthday + pId;
^
ReferenceError: birthday is not defined
at Object.fullId (C:\Users\Eunice\OneDrive - Sogang\바탕 화면\git\ai_webdev\js_ts\this_reference_error\8_object.js:7:9)
at Object.<anonymous> (C:\Users\Eunice\OneDrive - Sogang\바탕 화면\git\ai_webdev\js_ts\this_reference_error\8_object.js:10:8)
at Module._compile (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1254:14)
at Module._extensions..js (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1308:10)
at Module.load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:1117:32)
at Module._load (node:internal/modules/cjs/loader:958:12)
at Function.executeUserEntryPoint [as runMain] (node:internal/modules/run_main:81:12)
at node:internal/main/run_main_module:23:47
Node.js v18.15.0
단, 아래와 같이 함수를 호출하면 정상 결과가 나타난다.
person.fullId;
RESULT
올해는 2023년입니다.
설명
ReferenceError 발생 원인
- 객체는 현재 범위에서 존재하지 않거나 (non-existing),
- 초기화되지 않은 (not initialized) 변수를 참조했을 때 발생하는 에러
this
- 객체 내부에서 사용될 때 현재 해당 객체(current object)를 가리킨다
코드 안에서 this는 person 객체 안에서 사용되었으니
this는 person을 참조하게 된다.
–> this.birthday는 person의 birthday 속성을을 가리킨다.
괄호 ‘()‘를 사용하여 fullId 함수 호출
person.fullId()
- 위 방식대로
fullID함수를 호출하면 이 함수가 person 객체의 함수로 호출된다. - 원래 코드에서
return this.birthday + this.pId를 쓰면this는person객체를 가리키고,this.birthday와this.pId는person의birthday와pID프로포티를 가리킨다. - 이 경우
return birthday + pId와 같이this.를 안 붙이고 접근을 시도하면 JS 인터프리터는birthday와pId를person객체의 property가 아닌fullId함수 안에 정의된 변수들이라고 가정할 것이다.fullId안에서birthday와pId라는 변수가 선언되지 않았으니 정의가 없으며undefined가 된다. 이 때문에ReferenceError가 발생된다.- 자바스크립트에서
this.를 붙여서 범위(scope) 또는 문맥(context)를 알려주지 않으면 인터프리터는 현재 범위(current scope)부터 상위 범위(parent scope), 그리고 전역 범위(global scope)까지 탐색하여 해당 변수를 찾는다. (fullId함수는person객체 범위 안에 있으니fullId의 현재 범위는 함수 안의 범위이고 상위 범위는 전역 범위(global)이다.birthday와pId는 함수 안에 그리고 전역적으로 정의되어 있지 않기 때문에 인터프리터가 변수들을 찾지 못하는 상황이 되며 ReferenceError의 원인이 된다.)
- 자바스크립트에서
따라서 person.fullId()로 호출할 때 this.birthday와 this.pId를 사용해야 person 객체의 property를 참조하면 ReferenceError 가 발생하지 않는다.
괄호 ‘()’ 없이 fullId 함수 호출
person.fullId;
- 위 방식의 경우
person.fullId는 함수를 호출 또는 실행시키지 않고 참조만 하는 방식이다. - 함수를 호출하지 않고 참조만 하기 때문에 함수의 문맥(context) 즉 this의 값이 중요하지 않다. 따라서
fullId함수 안에서birthday와pId속성에 접근하려는 시도를 하지 않으며,return birthday + pId를 사용해도 ReferenceError가 발생하지 않는다.
요약
person.fullId();
- person 객체의 메서드로서 함수를 호출한다.
fullId함수 내부의this키워드는person객체를 가리키며,this.birthday와this.pId에 접근할 수 있다.
person.fullId;
- 함수 자체를 반환하며 호출하지 않는다.
- 함수는 참조만 되고 실행되지 않기 때문에 오류가 발생하지 않는다.
SOURCE CODE
https://github.com/ganyunhee/ai_webdev/tree/main/js_ts/this_reference_error
과제 > 오목게임 (Day 7 continuation)
- 기능 추가 : 승패가 계속 나지 않을 경우 실행 후 5분이 지나면 자동 종료시킨다.
ISSUE. Player 1 always wins (output typo)
I noticed that the program always prints out that Player 1 wins even when Player 2 wins… And then I found a typo in the output. Whoops!
Before changes:
console.log(`GAME OVER. Player ${currentPlayer === 1 ? '1' : '1'} wins!`);
After changes:
console.log(`GAME OVER. Player ${currentPlayer === 1 ? '1' : '2'} wins!`);
Current Code
let board: string[][] = [];
var row = 0;
var col = 0;
// FUNCTION. initialize 30x30 board with '-'
function init() {
// traverse rows
for (let i=0; i < 30; i++) {
const row: string[] = [];
// traverse columns
for (let j=0; j < 30; j++) {
row.push('-');
}
board.push(row);
}
}
// FUNCTION. print out board contents
function output() {
for (const row of board) {
console.log(row.join(' '));
}
}
// FUNCTION. update the board
// -- based on player input
function update(row: number, col: number, player: number) {
if(board[row][col] === '-') {
board[row][col] = player === 1 ? 'B' : 'W';
return true;
}
return false;
}
// FUNCTION. get user input (continuous)
async function getPlayerInput(player: number) {
// import readline module
const rl = require('readline').createInterface ({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout
});
// read and return user input
return new Promise<string>((resolve) => {
rl.question(`Player ${player}'s turn (row col): `, (response) => {
rl.close();
resolve(response);
});
});
}
// FUNCTION. Check if player wins
// -- win condition logic :
// -- check if any row, column, diagonal has five matching symbols
function checkWinCondition(): boolean {
// check rows
for (let i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
let countB = 0;
let countW = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
if (board[i][j] === 'B') {
countB++;
countW = 0;
} else if (board[i][j] === 'W') {
countW++;
countB = 0;
} else {
countB = 0;
countW = 0;
}
if (countB === 5 || countW === 5) {
return true;
}
}
}
// check columns
for (let j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
let countB = 0;
let countW = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
if (board[i][j] === 'B') {
countB++;
countW = 0;
} else if (board[i][j] === 'W') {
countW++;
countB = 0;
} else {
countB = 0;
countW = 0;
}
if (countB === 5 || countW === 5) {
return true;
}
}
}
// check diagonals
for (let i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
// check diagonals
// start from (i, j) going right and down
let countB = 0;
let countW = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
if (i + k < 30 && j + k < 30) {
if (board[i + k][j + k] === 'B') {
countB++;
countW = 0;
} else if (board[i + k][j + k] === 'W') {
countW++;
countB = 0;
} else {
countB = 0;
countW = 0;
}
if (countB === 5 || countW === 5) {
return true;
}
}
}
// Check diagonals starting from position (i, j) going right and up
countB = 0;
countW = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
if (i - k >= 0 && j + k < 30) {
if (board[i - k][j + k] === 'B') {
countB++;
countW = 0;
} else if (board[i - k][j + k] === 'W') {
countW++;
countB = 0;
} else {
countB = 0;
countW = 0;
}
if (countB === 5 || countW === 5) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// FUNCTION. play
// -- continuosly prompt to get user input and check for winner
async function playGame() {
// initialize
init();
let currentPlayer = 1;
// check for win
while (!checkWinCondition()) {
// print board
output();
// await user input
const input = await getPlayerInput(currentPlayer);
const [row, col] = input.split(' ').map((coord) => parseInt(coord));
// check for valid moves
if (row >= 0 && row < 30 && col >= 0 && col < 30) {
const validMove = update(row, col, currentPlayer);
if (validMove) {
currentPlayer = currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1;
} else {
console.log('Invalid move. Try again.');
}
} else {
console.log('Invalid input. Try again.');
}
}
// end game
output();
console.log(`GAME OVER. Player ${currentPlayer === 1 ? '1' : '2'} wins!`);
}
// run game
// -- if error persists, print error
playGame().catch((error) => console.error(error));
Step 6. Add Timer
Add flags
Inside the playGame() async function,
Add flag to track if the game is won
let isGameWon = false;
Add flag to track if timeout is reached
let isTimeout = false;
Add functions to set flags
Inside the playGame() async function,
Add function to check for win condition and change flag if there is a winner.
function checkAndSetGameWon() {
if(checkWinCondition()) {
isGameWon = true;
}
}
Add function to change timeout flag.
function handleTimeout() {
isTimeout = true;
output();
console.log("DRAW. Five minutes have passed. No player has won.");
}
Add timer via setTimeout()
To add a timer, I used the JavaScript function setTimeout()
setTimeout(code, delay)
//OR
setTimeout(functionRef, delay)
setTimeout()
- sets a timer, then executes a function or code after timer expires ref. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/setTimeout
setTimeout(handleTimeout, 5 * 60 * 1000);
Here, the timer is set to five minutes converted into milliseconds
5 * 60 to convert minutes to seconds, then
(5 * 60) * 1000 to convert seconds to milliseconds
After the delay, setTimeout() then calls handleTimeout().
NOTE. This timer does not restart after every user input and counts five minutes for the entirety of game. In short, players can play only until five minutes.
Change conditions for pre-existing while loop
To make the game loop until the game is won, I called the checkWinCondition() throughout the while loop in my previous code. I now need to loop until the game is won or until the timer expires.
Since I’ve made the checkAndSetGameWon() function to check if the player wins by calling checkWinCondition() and setting the isGameWon flag that indicates if a player wins, I will only need to check the flag in the while loop.
This goes the same for the timeout flag. And so we have the following conditions for the while loop.
while (!isGameWon && !isTimeout) {
...
}
Since I now have a separate function that checks the game status and sets the win flag, I have to call it for every valid move a player makes in order to check if the player is making a move that wins the game.
So I modified the conditions for checking valid moves as follows:
if (row >= 0 && row < 30 && col >= 0 && col < 30) {
const validMove = update(row, col, currentPlayer);
if (validMove) {
currentPlayer = currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1;
checkAndSetGameWon(); // check if player makes a winning move
} else {
console.log('Invalid move. Try again.');
}
} else {
console.log('Invalid input. Try again.');
}
ISSUE. Continuous timer even after the game has ended
The timer kept counting for five minutes even after a player has won, and when the timer expires, it prints out a message resulting to the following.
GAME OVER. Player 1 wins!
DRAW. Five minutes have passed. No player has won.
I found a JavaScript function that can clear the timeout to prevent handleTimeout() from executing after game ends.
clearTimeout(timeoutID)
clearTimeout()
- cancels a timeout previously established by
setTimeout()ref. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/clearTimeout
So I used the setTimeout() function as an object and put it into a constant variable named timeout.
const timeout = setTimeout(handleTimeout, 5 * 60 * 1000);
Then cleared that timeout just before printing the last changes to the board (after a player’s winning turn) and ending the game with a “Player # wins” message.
clearTimeout(timeout);
RESULT

ISSUE. Game does not end even after timer expires
The program asks for one last input and considers valid input as an invalid move before ending the game.
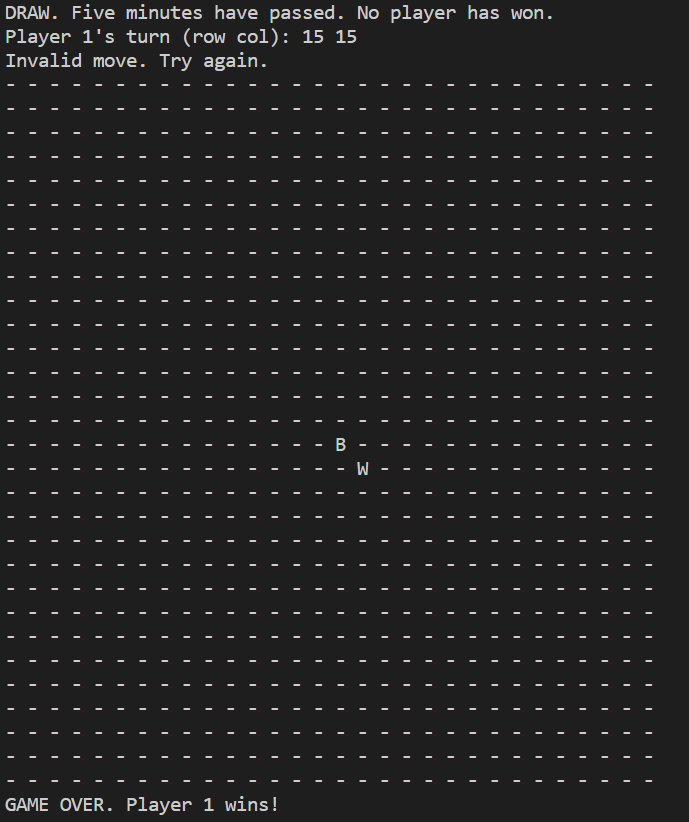
I added return at the end of the handleTimeout() function in order for it to end the playGame() function after the timer expires.
function handleTimeout() {
isTimeout = true;
output();
console.log("DRAW. Five minutes have passed. No player has won.");
return;
}
RESULT

SOURCE CODE
https://github.com/ganyunhee/ai_webdev/tree/main/js_ts/omok_game
——————————————————————————
본 후기는 정보통신산업진흥원(NIPA)에서 주관하는 <AI 서비스 완성! AI+웹개발 취업캠프 - 프론트엔드&백엔드> 과정 학습/프로젝트/과제 기록으로 작성 되었습니다. #정보통신산업진흥원 #NIPA #AI교육 #프로젝트 #유데미 #IT개발캠프 #개발자부트캠프 #프론트엔드 #백엔드 #AI웹개발취업캠프 #취업캠프 #개발취업캠프